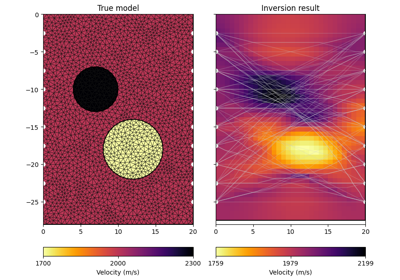
pygimli.physics.traveltime#
First-arrival traveltime
e.g. refraction or crosshole seismics and GPR
Classes:
TravelTimeManager
RefractionNLayer
DataContainer[TT]
Main entry functions:
load - load or import from various formats
createRAData - create refraction data scheme
simulate - synthetic model computation
show - show first arrivals als curves or image
Overview#
Functions
|
Create crosshole scheme assuming two boreholes with equal sensor numbers. |
|
Create 2D velocity gradient model. |
|
Create a refraction data container. |
|
Plot first arrivals as lines. |
|
Draw first arrival traveltime data into mpl ax a. |
|
Draw apparent velocities as matrix into an axis. |
|
Shortcut to load TravelTime data. |
|
Distance vector between shot and for each 's' and 'g' in data. |
|
Show data. |
|
Show apparent velocity as image plot. |
|
Simulate traveltime measurements. |
Classes
|
Data Container for traveltime. |
Dijkstras shortest path finding |
|
|
Forward operator for 1D Refraction seismic with layered model. |
|
FOP for 1D Refraction seismic with layered model (e.g. water layer). |
|
Forward modelling class for traveltime using Dijktras method. |
|
Manager for refraction seismics (traveltime tomography). |
Functions#
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.createCrossholeData(sensors=None, x=None, z=None)[source]#
Create crosshole scheme assuming two boreholes with equal sensor numbers.
- Parameters:
sensors (array (Nx2)) – Array with position of sensors. Alternatively, specify x and z
x (iterable [M]) – horizontal positions of boreholes
z (iterable [M]) – vertical positions of sensors in each borehole
- Returns:
scheme – Data container with sensors predefined sensor indices ‘s’ and ‘g’ for shot and receiver numbers.
- Return type:
Examples using pygimli.physics.traveltime.createCrossholeData
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.createGradientModel2D(data, mesh, vTop, vBot, flat=False)[source]#
Create 2D velocity gradient model.
Creates a smooth, linear, starting model that takes the slope of the topography into account. This is done by fitting a straight line and using the distance to that as the depth value.
- Parameters:
data (pygimli DataContainer) – The topography list is in here.
mesh (pygimli.Mesh) – The parametric mesh used for the inversion
vTop (float) – The velocity at the surface of the mesh
vBot (float) – The velocity at the bottom of the mesh
- Returns:
model – A numpy array with slowness values that can be used to start the inversion.
- Return type:
pygimli Vector, length M
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.createRAData(sensors, shotDistance=1)[source]#
Create a refraction data container.
Default data container for shot and geophon at every sensor position. Predefined sensor indices’s ‘s’ as shot position and ‘g’ as geophon position.
- Parameters:
sensors (ndarray | R3Vector) – Geophon and shot positions (same)
shotDistances (int [1]) – Distance between shot indices.
- Returns:
data – Data container with predefined sensor indices ‘s’ and ‘g’ for shot and receiver numbers.
- Return type:
Examples using pygimli.physics.traveltime.createRAData
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.drawFirstPicks(ax, data, tt=None, plotva=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot first arrivals as lines.
- Parameters:
ax (matplotlib.axes) – axis to draw the lines in
data (GIMLI::DataContainer) – data containing shots (“s”), geophones (“g”) and traveltimes (“t”). (:py:class:pygimli.physics.traveltime.DataContainerTT.)
- Returns:
gci – list of plotting items (matplotlib lines)
- Return type:
list
Examples using pygimli.physics.traveltime.drawFirstPicks
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.drawTravelTimeData(ax, data, t=None)[source]#
Draw first arrival traveltime data into mpl ax a.
data of type pg.DataContainer must contain sensorIdx ‘s’ and ‘g’ and thus being numbered internally [0..n)
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.drawVA(ax, data, vals=None, usePos=True, pseudosection=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Draw apparent velocities as matrix into an axis.
- Parameters:
ax (mpl.Axes)
data (pg.physics.traveltime.DataContainerTT()) – Datacontainer with ‘s’ and ‘g’ Sensorindieces and ‘t’ traveltimes.
usePos (bool [True]) – Use sensor positions for axes tick labels
pseudosection (bool [False]) – Show in pseudosection style.
vals (iterable) – Traveltimes, if None data need to contain ‘t’ values.
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.load(fileName, verbose=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Shortcut to load TravelTime data.
Import Data and try to assume the file format.
- Parameters:
fileName (str)
- Returns:
data
- Return type:
pg.DataContainer
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.shotReceiverDistances(data, full=True)[source]#
Distance vector between shot and for each ‘s’ and ‘g’ in data.
- Parameters:
data (pg.DataContainerERT)
full (bool [True]) – Get distances between shot and receiver position when full is True or only form x coordinate if full is False
- Returns:
dists – Array of distances
- Return type:
array
Examples using pygimli.physics.traveltime.show
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.showVA(data, usePos=True, ax=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Show apparent velocity as image plot.
- Parameters:
data (pg.DataContainer()) – Datacontainer with ‘s’ and ‘g’ Sensorindieces and ‘t’ traveltimes.
Examples using pygimli.physics.traveltime.showVA
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.simulate(mesh, scheme, slowness=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Simulate traveltime measurements.
Perform the forward task for a given mesh, a slowness distribution (per cell) and return data (traveltime) for a measurement scheme.
- Parameters:
mesh (GIMLI::Mesh) – Mesh to calculate for or use the last known mesh.
scheme (GIMLI::DataContainer) – Data measurement scheme needs ‘s’ for shot and ‘g’ for geophone data token.
slowness (array(mesh.cellCount()) | array(N, mesh.cellCount())) –
Slowness distribution for the given mesh cells can be:
a single array of len mesh.cellCount()
a matrix of N slowness distributions of len mesh.cellCount()
a slowness map [[marker0, slow0], [marker1, slow1], …]
vel (array(mesh.cellCount()) | array(N, mesh.cellCount())) – Velocity distribution for the mesh cells (overwrites slowness!).
secNodes (int [2]) – Number of refinement nodes to increase accuracy of the forward calculation.
noiseLevel (float [0.0]) – Add relative noise to the simulated data. noiseLevel*100 in %
noiseAbs (float [0.0]) – Add absolute noise to the simulated data in ms.
seed (int [None]) – Seed the random generator for the noise.
- Keyword Arguments:
returnArray ([False]) – Return only the calculated times.
verbose ([self.verbose]) – Overwrite verbose level.
**kwargs – Additional kwargs …
- Returns:
t – The resulting simulated travel time values (returnArray=True) or DataContainer containing them in t field (returnArray=False). Either one column array or matrix in case of slowness matrix.
- Return type:
array(N, data.size()) | DataContainer
Examples using pygimli.physics.traveltime.simulate
Classes#
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.DataContainer#
alias of
DataContainerTT
- class pygimli.physics.traveltime.DataContainerTT(data=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
DataContainerData Container for traveltime.
- class pygimli.physics.traveltime.Dijkstra#
Bases:
instanceDijkstras shortest path finding
- class DistancePair_#
Bases:
instanceDefinition for the priority queue
- __init__((object)arg1) object :#
- C++ signature :
void* __init__(_object*)
__init__( (object)arg1, (object)f, (object)s) -> object :
- C++ signature :
void* __init__(_object*,double,GIMLI::Dijkstra::Edge_ {lvalue})
- property first#
- property second#
- class Edge_#
Bases:
instance- __init__((object)arg1) object :#
- C++ signature :
void* __init__(_object*)
__init__( (object)arg1, (object)a, (object)b) -> object :
- C++ signature :
void* __init__(_object*,unsigned long,unsigned long)
- property end#
- property start#
- __init__((object)arg1) object :#
- C++ signature :
void* __init__(_object*)
__init__( (object)arg1, (object)graph) -> object :
- C++ signature :
void* __init__(_object*,std::map<unsigned long, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > >, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > > > > >)
- distance((object)arg1, (object)root, (object)node) object :#
Distance from root to node.
- C++ signature :
double distance(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long,unsigned long)
- distance( (object)arg1, (object)node) -> object :
Distance to node to the last known root.
- C++ signature :
double distance(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long)
- distances((object)arg1, (object)root) object :#
All distances to root.
- C++ signature :
GIMLI::Vector<double> distances(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long)
- distances( (object)arg1) -> object :
All distances from to last known root.
- C++ signature :
GIMLI::Vector<double> distances(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue})
- graph((object)arg1) object :#
- C++ signature :
std::map<unsigned long, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > >, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > > > > > {lvalue} graph(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue})
graph( (object)arg1) -> object :
- C++ signature :
std::map<unsigned long, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > >, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > > > > > graph(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue})
- graphInfo((object)arg1, (object)na, (object)nb) object :#
- C++ signature :
GIMLI::GraphDistInfo graphInfo(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long,unsigned long)
- setGraph((object)arg1, (object)graph) object :#
- C++ signature :
void* setGraph(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},std::map<unsigned long, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > >, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, std::map<unsigned long, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo, std::less<unsigned long>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long const, GIMLI::GraphDistInfo> > > > > >)
- setStartNode((object)arg1, (object)startNode) object :#
- C++ signature :
void* setStartNode(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long)
- shortestPath((object)arg1, (object)start, (object)end) object :#
Get the shortest way from node index start to end.
- C++ signature :
GIMLI::Vector<unsigned long> shortestPath(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long,unsigned long)
- shortestPathTo((object)arg1, (object)node, (object)way) object :#
Get the shortest way from root to node. Inline version.
- C++ signature :
void* shortestPathTo(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long,GIMLI::Vector<unsigned long> {lvalue})
- shortestPathTo( (object)arg1, (object)node) -> object :
Get the shortest way from root to node.
- C++ signature :
GIMLI::Vector<unsigned long> shortestPathTo(GIMLI::Dijkstra {lvalue},unsigned long)
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.Manager#
alias of
TravelTimeManager
- class pygimli.physics.traveltime.RefractionNLayer(offset=0, nlay=3, vbase=1100, verbose=True)[source]#
Bases:
ModellingBaseMT__Forward operator for 1D Refraction seismic with layered model.
- class pygimli.physics.traveltime.RefractionNLayerFix1stLayer(offset=0, nlay=3, v0=1465, d0=200, muteDirect=False, verbose=True)[source]#
Bases:
ModellingBaseMT__FOP for 1D Refraction seismic with layered model (e.g. water layer).
- __init__(offset=0, nlay=3, v0=1465, d0=200, muteDirect=False, verbose=True)[source]#
Init forward operator for velocity increases with fixed 1st layer.
- Parameters:
offset (iterable) – vector of offsets between shot and geophone
nlay (int) – number of layers
v0 (float) – First layer velocity (at the same time base velocity)
d0 (float) – Depth of first layer in meter.
muteDirect (bool [False]) – Mute the direct arrivels fron the first layer.
- class pygimli.physics.traveltime.TravelTimeDijkstraModelling(**kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
MeshModellingForward modelling class for traveltime using Dijktras method.
- __init__(**kwargs)[source]#
Initialize.
- Variables:
fop (pg.frameworks.Modelling)
data (pg.DataContainer)
modelTrans ([pg.trans.TransLog()])
- Keyword Arguments:
**kwargs – fop: Modelling
- createRefinedFwdMesh(mesh)[source]#
Refine the current mesh for higher accuracy.
This is called automatic when accesing self.mesh() so it ensures any effect of changing region properties (background, single).
- createStartModel(dataVals)[source]#
Create a starting model from data values (gradient or constant).
- property dijkstra#
Return current Dijkstra graph associated to mesh and model.
- class pygimli.physics.traveltime.TravelTimeManager(data=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
MeshMethodManagerManager for refraction seismics (traveltime tomography).
TODO Document main members and use default MethodManager interface e.g., self.inv, self.fop, self.paraDomain, self.mesh, self.data
- __init__(data=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Create an instance of the Traveltime manager.
- Parameters:
data (GIMLI::DataContainer | str) – You can initialize the Manager with data or give them a dataset when calling the inversion.
- applyMesh(mesh, secNodes=None, ignoreRegionManager=False)[source]#
Apply mesh, i.e. set mesh in the forward operator class.
- createForwardOperator(**kwargs)[source]#
Create default forward operator for Traveltime modelling.
Your want your Manager use a special forward operator you can add them here on default Dijkstra is used.
- createMeshMovedToMeshManager(data=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Create default inversion mesh.
Inversion mesh for traveltime inversion does not need boundary region.
- Parameters:
data (DataContainer) – Data container to read sensors from.
- Keyword Arguments:
` (Forwarded to)
- createTraveltimefield(v=None, startPos=None, withSec=False)[source]#
Compute a single traveltime field.
- drawRayPaths(ax, model=None, rayPaths=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Draw the the ray paths for model or last model.
If model is not specified, the last calculated Jacobian is used.
- Parameters:
rayPaths (list of np.array) – x/y column array with ray point positions
model (array) – Velocity model for which to calculate and visualize ray paths (the default is model for last Jacobian calculation in self.velocity).
ax (matplotlib.axes object) – To draw the model and the path into.
**kwargs (type) – Additional arguments passed to LineCollection (alpha, linewidths, color, linestyles).
- Returns:
lc
- Return type:
matplotlib.LineCollection
- getRayPaths(model=None)[source]#
Compute ray paths.
If model is not specified, the last calculated Jacobian is used.
- Parameters:
model (array) – Velocity model for which to calculate and visualize ray paths (the default is model for last Jacobian calculation in self.velocity).
- Return type:
list of two-column array holding x and y positions
- invert(data=None, useGradient=True, vTop=500, vBottom=5000, secNodes=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Invert data.
- Parameters:
data (pg.DataContainer()) – Data container with at least SensorIndices ‘s g’ (shot/geophone) & data values ‘t’ (traveltime in s) and ‘err’ (absolute error in s)
useGradient (bool [True]) – Use gradient starting model typical for refraction cases. For crosshole tomography geometry you should set this to False for a non-gradient (e.g. homogeneous) starting model.
vTop (float) – Top velocity for gradient starting model.
vBottom (float) – Bottom velocity for gradient starting model.
secNodes (int [2]) – Number of secondary nodes for accuracy of forward computation.
- Returns:
Mapped (for paradomain) velocity model.
- Return type:
- Keyword Arguments:
kwargs (**) – Inversion related arguments: See
pygimli.frameworks.MeshMethodManager.invert
- saveResult(folder=None, size=(16, 10), verbose=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Save the results in a specified (or date-time derived) folder.
- Saved items are:
Resulting inversion model
Velocity vector
Coverage vector
Standardized coverage vector
Mesh (bms and vtk with results)
- Parameters:
path (str[None]) – Path to save into. If not set the name is automatically created
size ((float, float) (16,10)) – Figure size.
- Keyword Arguments:
showResults (Will be forwarded to)
- Returns:
Name of the result path.
- Return type:
str
- showFit(axs=None, firstPicks=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Show data fit as first-break picks or apparent velocity.
- showRayPaths(model=None, ax=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Show the model with ray paths for given model.
If not model specified, the last calculated Jacobian is taken.
- Parameters:
model (array) – Velocity model for which to calculate and visualize ray paths (the default is model for last Jacobian calculation in self.velocity).
ax (matplotlib.axes object) – To draw the model and the path into.
**kwargs (type) – forward to drawRayPaths
- Returns:
ax (matplotlib.axes object)
cb (matplotlib.colorbar object (only if model is provided))
Examples
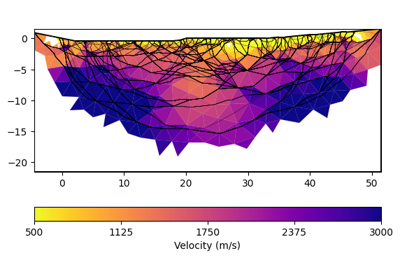
>>> import pygimli as pg >>> from pygimli.physics import traveltime as tt >>> >>> x, y = 8, 6 >>> mesh = pg.createGrid(x, y) >>> data = tt.createRAData([(0, 0)] + [(x, i) for i in range(y)], ... shotDistance=y+1) >>> data["t"] = 1.0 >>> mgr = tt.Manager(data) >>> mgr.applyMesh(mesh, secNodes=10) >>> ax, cb = mgr.showRayPaths(showMesh=True, diam=0.1)
- simulate(mesh=None, scheme=None, slowness=None, vel=None, seed=None, secNodes=2, noiseLevel=0.0, noiseAbs=0.0, **kwargs)[source]#
Simulate traveltime measurements.
Perform the forward task for a given mesh, a slowness distribution (per cell) and return data (traveltime) for a measurement scheme.
- Parameters:
mesh (GIMLI::Mesh) – Mesh to calculate for or use the last known mesh.
scheme (GIMLI::DataContainer) – Data measurement scheme needs ‘s’ for shot and ‘g’ for geophone data token.
slowness (array(mesh.cellCount()) | array(N, mesh.cellCount())) –
Slowness distribution for the given mesh cells can be:
a single array of len mesh.cellCount()
a matrix of N slowness distributions of len mesh.cellCount()
a slowness map [[marker0, slow0], [marker1, slow1], …]
vel (array(mesh.cellCount()) | array(N, mesh.cellCount())) – Velocity distribution for the mesh cells (overwrites slowness!).
secNodes (int [2]) – Number of refinement nodes to increase accuracy of the forward calculation.
noiseLevel (float [0.0]) – Add relative noise to the simulated data. noiseLevel*100 in %
noiseAbs (float [0.0]) – Add absolute noise to the simulated data in ms.
seed (int [None]) – Seed the random generator for the noise.
- Keyword Arguments:
returnArray ([False]) – Return only the calculated times.
verbose ([self.verbose]) – Overwrite verbose level.
**kwargs – Additional kwargs …
- Returns:
t – The resulting simulated travel time values (returnArray=True) or DataContainer containing them in t field (returnArray=False). Either one column array or matrix in case of slowness matrix.
- Return type:
array(N, data.size()) | DataContainer
- property velocity#
Return velocity vector (the inversion model).
- pygimli.physics.traveltime.TravelTimeModelling#
alias of
TravelTimeDijkstraModelling