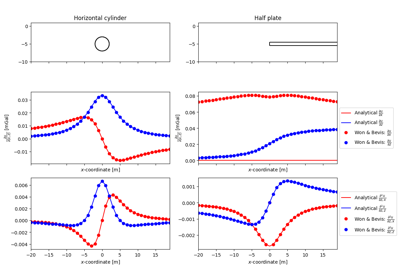
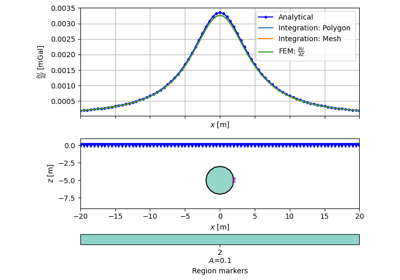
pygimli.physics.gravimetry#
Solve gravimetric and magneto static problems in 2D and 3D analytically
Overview#
Functions
|
Vertical magnetic gradient for polygone. |
|
Magnetic anomaly for a horizontal cylinder. |
|
Magnetic anomaly for a sphere. |
|
Solve gravity and/or magnetics problem after Holstein (1997). |
|
TODO WRITEME. |
|
TODO WRITEME. |
|
TODO WRITEME. |
|
2D Gradient of gravimetric potential of horizontal cylinder. |
|
Gravitational field od a horizontal half plate. |
|
Gravitational field of a sphere. |
|
Solve gravimetric response. |
|
Gravitational potential of horizonzal cylinder. |
|
Gravitational potential of a sphere. |
Classes
|
Magnetics modelling operator using Holstein (2007). |
|
Gravimetry modelling operator. |
|
Magnetics Manager. |
|
Magnetics modelling operator using Holstein (2007). |
|
Functions#
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.BZPoly(pnts, poly, mag, openPoly=False)[source]#
Vertical magnetic gradient for polygone.
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.BaZCylinderHoriz(pnts, R, pos, M)[source]#
Magnetic anomaly for a horizontal cylinder.
Calculate the vertical component of the anomalous magnetic field Bz for a buried horizontal cylinder at position pos with radius R for a given magnetization M at measurement points pnts.
TODO .. only 2D atm
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.BaZSphere(pnts, R, pos, M)[source]#
Magnetic anomaly for a sphere.
Calculate the vertical component of the anomalous magnetic field Bz for a buried sphere at position pos with radius R for a given magnetization M at measurement points pnts.
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.SolveGravMagHolstein(*args, **kwargs)#
Solve gravity and/or magnetics problem after Holstein (1997).
- Parameters:
mesh (pygimli:mesh) – tetrahedral or hexahedral mesh
pnts (list|array of (x, y, z)) – measuring points
cmp (list of str) – component list of type str, valid values are: gx, gy, gz, TFA, Bx, By, Bz, Bxx, Bxy, Bxz, Byy, Byz, Bzz
igrf (list|array of size 3 or 7) –
international geomagnetic reference field, either [D, I, H, X, Y, Z, F] - declination, inclination, horizontal field,
X/Y/Z components, total field OR
[X, Y, Z] - X/Y/Z components
- Returns:
out – kernel matrix to be multiplied with density or susceptibility
- Return type:
ndarray (nPoints x nComponents x nCells)
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradGZCylinderHoriz(r, a, rho, pos=(0.0, 0.0))[source]#
TODO WRITEME.
\[g = -grad u(r), with r = [x,z], |r| = \sqrt{x^2+z^2}\]
Examples using pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradGZCylinderHoriz
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradGZHalfPlateHoriz(pnts, t, rho, pos=(0.0, 0.0))[source]#
TODO WRITEME.
\[g = -\nabla u\]
Examples using pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradGZHalfPlateHoriz
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradGZSphere(r, rad, rho, pos=(0.0, 0.0, 0.0))[source]#
TODO WRITEME.
\[g = -\nabla u\]
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradUCylinderHoriz(r, a, rho, pos=(0.0, 0.0))[source]#
2D Gradient of gravimetric potential of horizontal cylinder.
\[g = -G[m^3/(kg s^2)] * dM[kg/m] * 1/r[1/m] * grad(r)[1/1] = [m^3/(kg s^2)] * [kg/m] * 1/m * [1/1] == m/s^2\]
Examples using pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradUCylinderHoriz
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradUHalfPlateHoriz(pnts, t, rho, pos=(0.0, 0.0))[source]#
Gravitational field od a horizontal half plate.
\[g = -grad u,\]- Parameters:
pnts
t
rho – Density in [kg/m^3]
- Returns:
z-component of g .. math:: nabla(partial u/partialvec{r})_z
- Return type:
gz
Examples using pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradUHalfPlateHoriz
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gradUSphere(r, rad, rho, pos=(0.0, 0.0, 0.0))[source]#
Gravitational field of a sphere.
\[g = -G[m^3/(kg s^2)] * dM[kg] * 1/r^2 1/m^2] * \grad(r)[1/1] = [m^3/(kg s^2)] * [kg] * 1/m^2 * [1/1] == m/s^2\]
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.solveGravimetry(mesh, dDensity=None, pnts=None, complete=False)[source]#
Solve gravimetric response.
2D with
pygimli.physics.gravimetry.lineIntegralZ_WonBevis3D with
pygimli.physics.gravimetry.gravMagBoundarySinghGup- Parameters:
mesh (GIMLI::Mesh) – 2d or 3d mesh with or without cells.
dDensity (float | array) –
Density difference.
- float – solve for positive boundary marker only.
Assuming one inhomogeneity.
[[int, float]] – solve for multiple positive boundaries TOIMPL
array – solve for one delta density value per cell
None – return per cell kernel matrix G TOIMPL
pnts ([[x_i, y_i]]) – List of measurement positions.
complete (bool [False]) – If True return whole solution or matrix for [dgx, dgy, dgz]
- Returns:
dg (array OR)
dz, dgz (arrays (if complete))
Examples using pygimli.physics.gravimetry.solveGravimetry
- pygimli.physics.gravimetry.uCylinderHoriz(pnts, rad, rho, pos=[0.0, 0.0])[source]#
Gravitational potential of horizonzal cylinder.
Classes#
- class pygimli.physics.gravimetry.GravityModelling(mesh, points, cmp=['gz'])[source]#
Bases:
MeshModellingMagnetics modelling operator using Holstein (2007).
- class pygimli.physics.gravimetry.GravityModelling2D(points=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
MeshModellingGravimetry modelling operator.
- __init__(points=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Initialize forward operator, optional with mesh and points.
You can specify both the mesh and the measuring points, or set the latter after the mesh has been set.
- Parameters:
mesh (pg.Mesh) – mesh for forward computation
points (array[x,y]) – measuring points
- class pygimli.physics.gravimetry.MagManager(data=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
MeshMethodManagerMagnetics Manager.
- createGrid(dx: float = 50, depth: float = 800, bnd: float = 0)[source]#
Create a grid.
- Parameters:
dx (float=50) – Grid spacing in x and y direction.
depth (float=800) – Depth of the grid in z direction.
bnd (float=0) – Boundary distance to extend the grid in x and y direction.
- Returns:
mesh – Created 3D structured grid.
- Return type:
- createMesh(bnd: float = 0, area: float = 100000.0, depth: float = 800, quality: float = 1.3, addPLC: Mesh = None, addPoints: bool = True)[source]#
Create an unstructured 3D mesh.
- Parameters:
bnd (float=0) – Boundary distance to extend the mesh in x and y direction.
area (float=1e5) – Maximum area constraint for cells.
depth (float=800) – Depth of the mesh in z direction.
quality (float=1.3) – Quality factor for mesh generation.
addPLC (GIMLI::Mesh) – PLC mesh to add to the mesh.
addPoints (bool=True) – Add points from self.x and self.y to the mesh.
- Returns:
mesh – Created 3D unstructured mesh.
- Return type:
- inversion(noise_level=2, noisify=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Run Inversion (requires mesh and FOP).
- Parameters:
noise_level (float|array) – absolute noise level (absoluteError)
noisify (bool) – add noise before inversion
relativeError (float|array [0.01]) – relative error to stabilize very low data
depthWeighting (bool [True]) – apply depth weighting after Li&Oldenburg (1996)
z0 (float) – skin depth for depth weighting
mul (array) – multiply constraint weight with
- Keyword Arguments:
startModel (float|array=0.001) – Starting model (typically homogeneous)
relativeError (float=0.001) – Relative error to stabilize very low data.
lam (float=10) – regularization strength
verbose (bool=True) – Be verbose
symlogThreshold (float [0]) – Threshold for symlog data trans.
C (int|Matrix|[float, float, float] [1]) – Constraint order.
C(,cType) (int|Matrix|[float, float, float]=C) – Constraint order, matrix or correlation lengths.
z0 (float=25) – Skin depth for depth weighting.
depthWeighting (bool=True) – Apply depth weighting after Li&Oldenburg (1996).
mul (float=1) – Multiply depth weighting constraint weight with this factor.
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments for the inversion.
- Returns:
model – Model vector (also saved in self.inv.model).
- Return type:
np.array
- show3DModel(label: str = None, trsh: float = 0.025, synth: Mesh = None, invert: bool = False, position: str = 'yz', elevation: float = 10, azimuth: float = 25, zoom: float = 1.2, **kwargs)[source]#
Standard 3D view.
- Parameters:
label (str='sus') – Label for the mesh data to visualize.
trsh (float=0.025) – Threshold for the mesh data to visualize.
synth (:gimliapi:`GIMLI::Mesh`=None) – Synthetic model to visualize in wireframe.
invert (bool=False) – Invert the threshold filter.
position (str="yz") – Camera position, e.g. “yz”, “xz”, “xy”.
elevation (float=10) – Camera elevation angle.
azimuth (float=25) – Camera azimuth angle.
zoom (float=1.2) – Camera zoom factor.
- Keyword Arguments:
cMin (float=0.001) – Minimum color value for the mesh data.
cMax (float=None) – Maximum color value for the mesh data. If None, it is set to the maximum value of the mesh data.
cMap (str="Spectral_r") – Colormap for the mesh data visualization.
logScale (bool=False) – Use logarithmic scale for the mesh data visualization.
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments for the pyvista plot.
- Returns:
pl – Plot widget with the 3D model visualization.
- Return type:
pyvista Plotter
- class pygimli.physics.gravimetry.MagneticsModelling(mesh=None, points=None, cmp=['TFA'], igrf=[0, 0, 50000])[source]#
Bases:
MeshModellingMagnetics modelling operator using Holstein (2007).
- __init__(mesh=None, points=None, cmp=['TFA'], igrf=[0, 0, 50000])[source]#
Setup forward operator.
- Parameters:
mesh (pygimli:mesh) – Tetrahedral or hexahedral mesh.
points (list|array of (x, y, z)) – Measuring points.
cmp ([str,]) – Component of: gx, gy, gz, TFA, Bx, By, Bz, Bxy, Bxz, Byy, Byz, Bzz
igrf (list|array of size 3 or 7) –
International geomagnetic reference field. either:
- [D, I, H, X, Y, Z, F] - declination,
inclination, horizontal field, X/Y/Z components, total field OR
- [X, Y, Z] - X/Y/Z
components OR
- [lat, lon] - latitude,
longitude (automatic by pyIGRF)
- class pygimli.physics.gravimetry.RemanentMagneticsModelling(mesh, points, cmp=['Bx', 'By', 'Bz'], igrf=[0, 0, 50000])[source]#
Bases:
MagneticsModelling- __init__(mesh, points, cmp=['Bx', 'By', 'Bz'], igrf=[0, 0, 50000])[source]#
Setup forward operator.
- Parameters:
mesh (pygimli:mesh) – Tetrahedral or hexahedral mesh.
points (list|array of (x, y, z)) – Measuring points.
cmp ([str,]) – Component of: gx, gy, gz, TFA, Bx, By, Bz, Bxy, Bxz, Byy, Byz, Bzz
igrf (list|array of size 3 or 7) –
International geomagnetic reference field. either:
- [D, I, H, X, Y, Z, F] - declination,
inclination, horizontal field, X/Y/Z components, total field OR
- [X, Y, Z] - X/Y/Z
components OR
- [lat, lon] - latitude,
longitude (automatic by pyIGRF)